FAQ on Food Waste to Biogas
This Page lists FAQ related to food Waste to Biogas. The process, parameters, usefulness etc.
Frequently Asked Question related to Food Waste to Biogas
Biogas is produced when organic matter biodegrades under anaerobic conditions (that is, in the absence of oxygen). This process produces a mixture of gases – primarily methane, with some carbon dioxide and tiny portions of other gases such as hydrogen sulphide.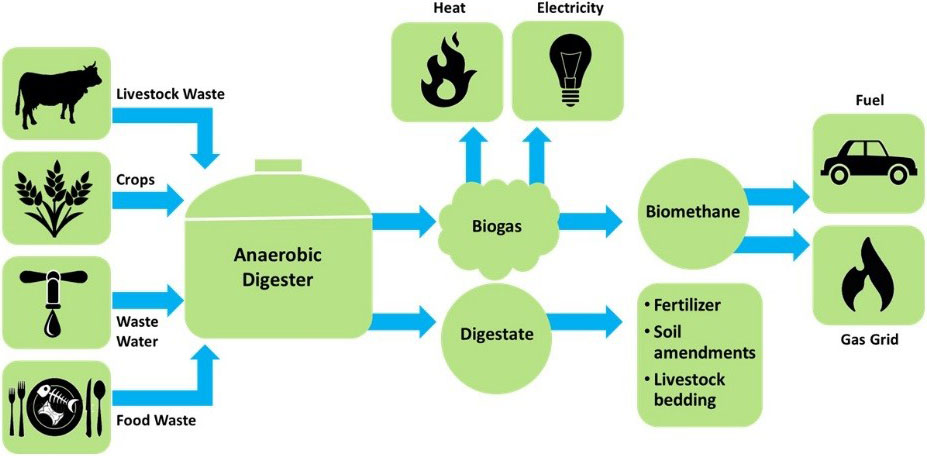
The food waste includes both food preparation waste (uncut vegetables, etc) and cooked food waste from the cafeteria (leftover food from plates) and the kitchen (cooked extra food).
100 Kgs of food waste can produce about 7 Kgs of Biogas
Apart from biogas, the food waste to biogas plants generate digestate, which can be used as fertiliser fields, gardens.
Methane has a greenhouse gas (GHG) heating factor 21 times higher than CO2. Combustion of biogas converts methane into CO2 and reduces the GHG impact by over 20 times. By extracting methane out of waste and using it to produce heat and/or electricity you ensure that the waste will not degrade in an open environment, therefore you are reducing direct methane atmospheric emissions.
The Costing of biogas plants depends on various factors such as size, location of plant, civil works required, length of pipes required etc. and hence, it can be best arrived by taking help of experts.
A food waste to biogas plant with daily processing capacity of 100 Kgs requires about 50 square meters of space.
